INJECTION MOLDING
INJECTION MOLDING
Most Commonly Used Manufacturing Process for The Fabrication of Plastic Parts
At Arion, we are committed to achieve total customer satisfaction through our services related to Automotive Moulded Components and by continual improvement of our quality through.
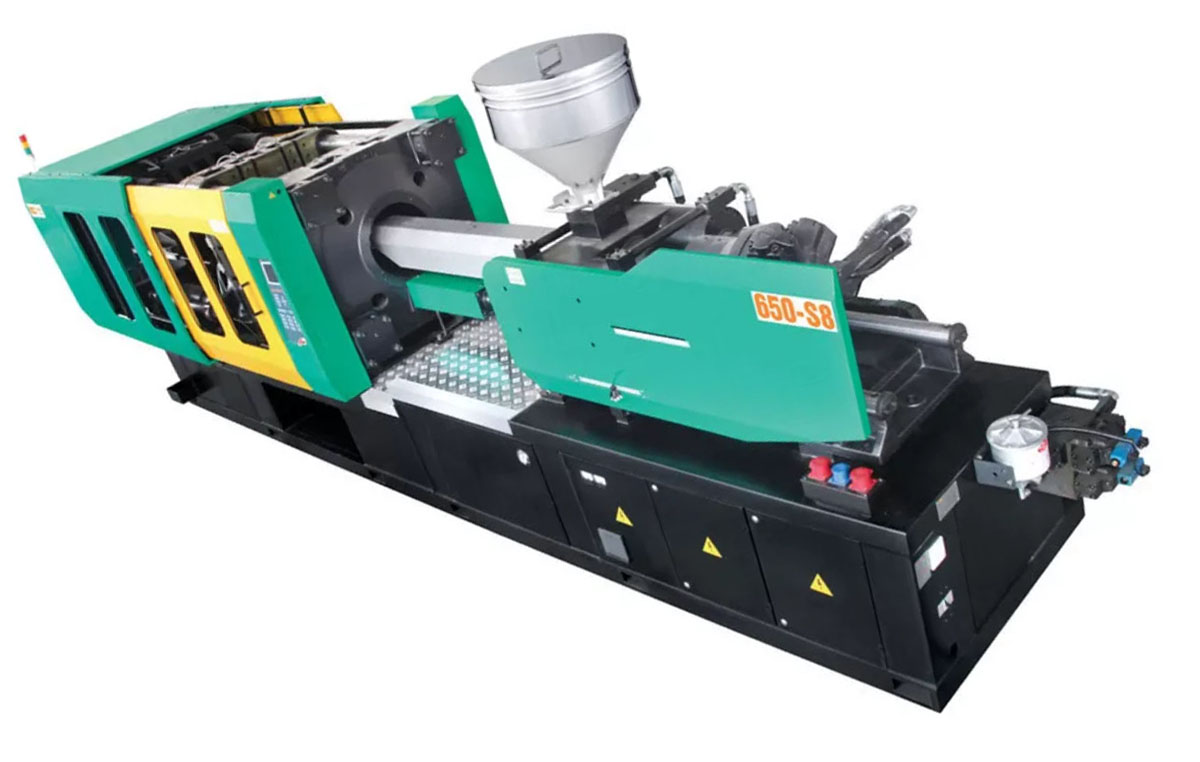
At Arion Technology Ltd. we specialize in producing high-quality plastic injection molded parts and mold tools. We offer machining and finishing services to make tools from a variety of materials and can produce 100 to 100,000+ finished parts in a wide variety of plastics. With advanced material verification and quality processes, we can ensure your tools and parts exceed your expectations. We offer a powerful technology with its hydromechanical twin-platen design and single-piston injection system. Injection Molding is one of the preferred methods for manufacturing parts because it has multiple advantages over other methods of plastic molding.
Advantages Of Plastic Injection Molding
There are many advantages to plastic injection molding. These include the ability to make large volumes of parts quickly, high surface quality, many resins to choose from, and durable tooling that can last for years.
Thousands of plastic materials
Make large volumes fast

Stable and reliable process

Excellent surface quality

Overmolding for more designs
Long-lasting tools
Plastic Injection Moulding Process
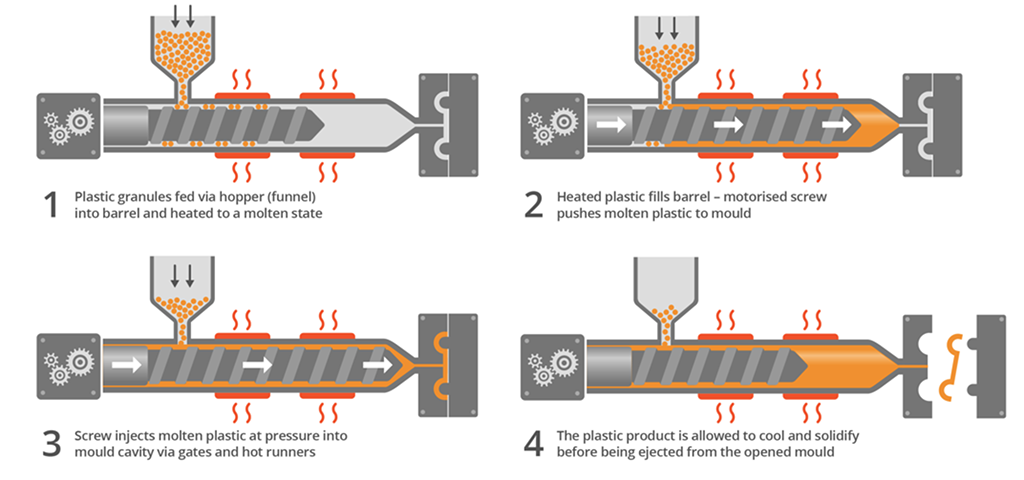
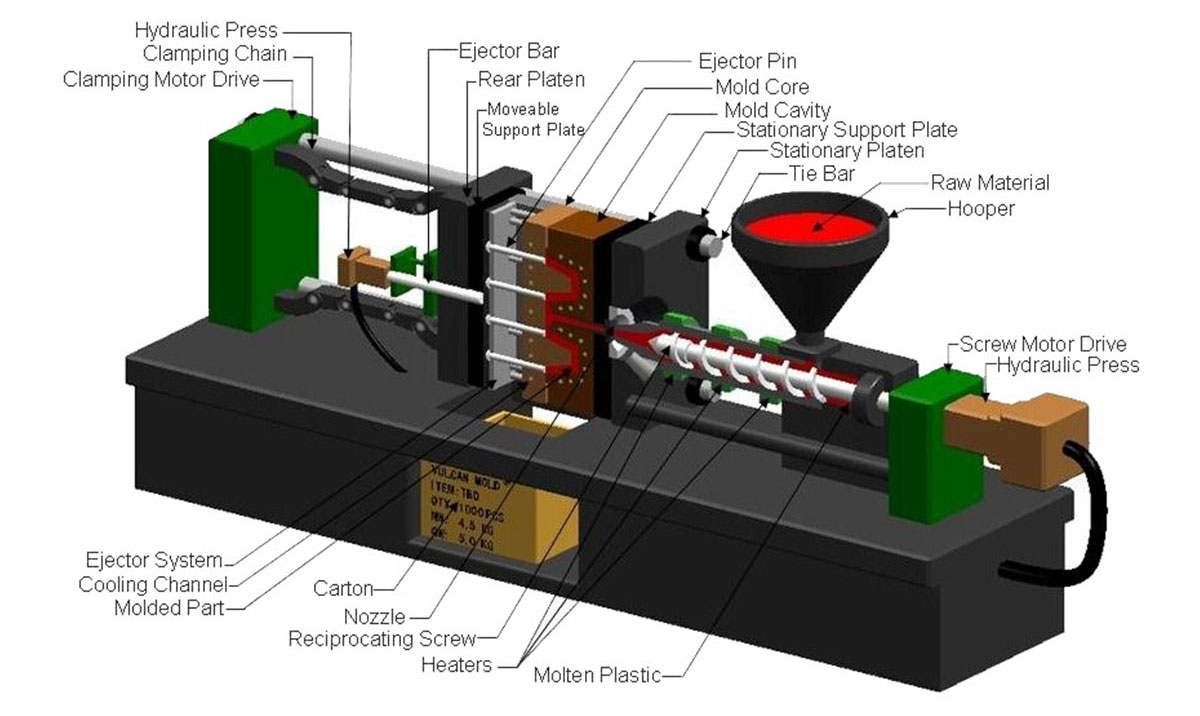
Plastic injection molding is a commonly used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts. The injection molding process requires the use of an injection molding machine, raw plastic material, and a mold. Raw plastic material is fed into a heated barrel, melted, mixed , and then injected into a mold cavity, where it cools and hardens into the shape of the mold.
- Clamping: The mold contains two halves of core and cavity. They must be securely closed by the clamping unit. One half is fixed and another is able to slide. The hydraulically powered clamping unit exerts enough force to keep the mold securely closed while the material is injected. The time required to close is dependent upon machine type.
- Injection: The raw plastic material, usually in the form of pellets is fed to the injection molding machine by the injection unit. During this process, the material is melted by heat and pressure from the feeding screw. The molten plastic is then injected into the mold very quickly and a build-up of pressure packs and holds the material. The amount of material injected is called a shot. The time required to inject the molten plastic is difficult to calculate accurately due to the complex and shifting flow of the molten plastic into the mold. However, the injection time can be estimated by the shot volume, injection pressure, and injection power.
- Cooling: Molten plastic kept inside the mold is let to cool when it contacts the inner surfaces of the mold. As the plastic cools, it will solidify into the shape of the desired part. The mold cannot be opened until the required cooling time has elapsed. The cooling time can be estimated from several thermodynamic properties of the plastic and the maximum wall thickness of the part.
- Ejection: After enough time has passed, the cooled part may be ejected from the mold by the ejection system, which is attached to the rear half of the mold. When the mold is opened, a mechanism is used to push the part out of the mold. Force must be applied to eject the part because during cooling the part shrinks and adheres to the mold. In order to facilitate the ejection of the part, a mold release agent can be sprayed onto the surfaces of the mold cavity prior to the injection of the material. The time that is required to open the mold and eject the part can be estimated from the dry cycle time of the machine and should include time for the part to fall free of the mold. Once the part is ejected, the mold can be clamped shut for the next shot to be injected.

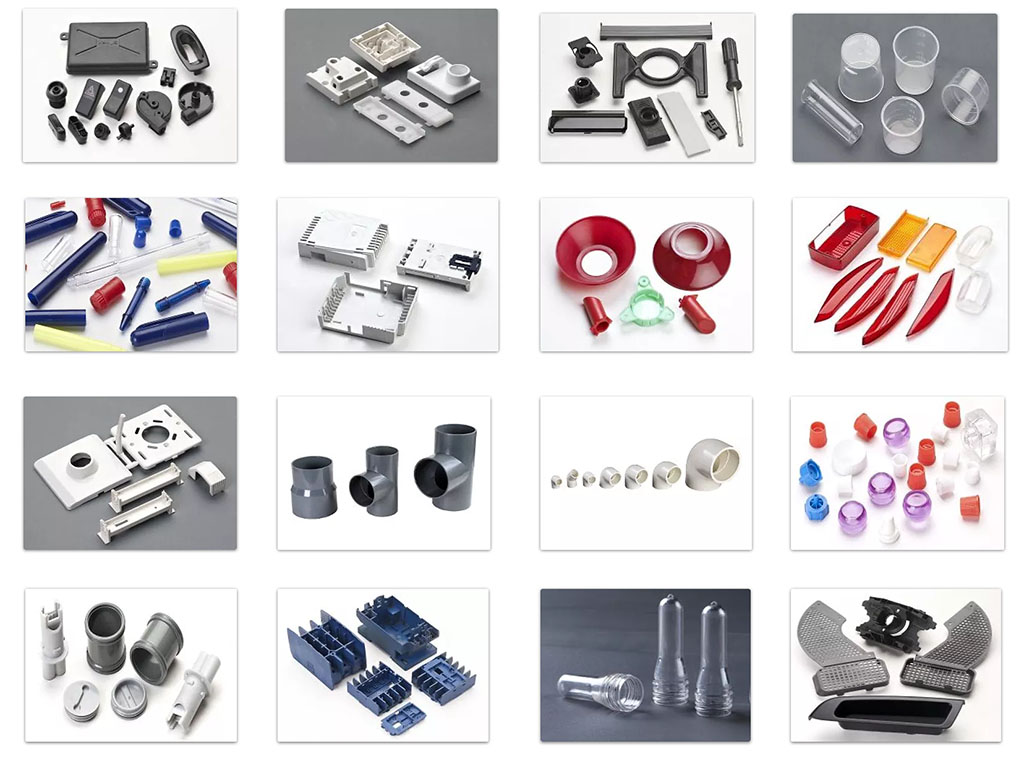
Applications of Induction Molding
Injection molding is used to produce thin-walled plastic parts for a wide variety of applications, one of the most common being plastic housings. Plastic housing is a thin-walled enclosure, often requiring many ribs and bosses on the interior. These housings are used in a variety of products including household appliances, consumer electronics, power tools, and as automotive dashboards. Other common thin-walled products include different types of open containers, such as buckets. Injection molding is also used to produce several everyday items such as toothbrushes or small plastic toys. Many medical devices, including valves and syringes, are manufactured using injection molding as well.




